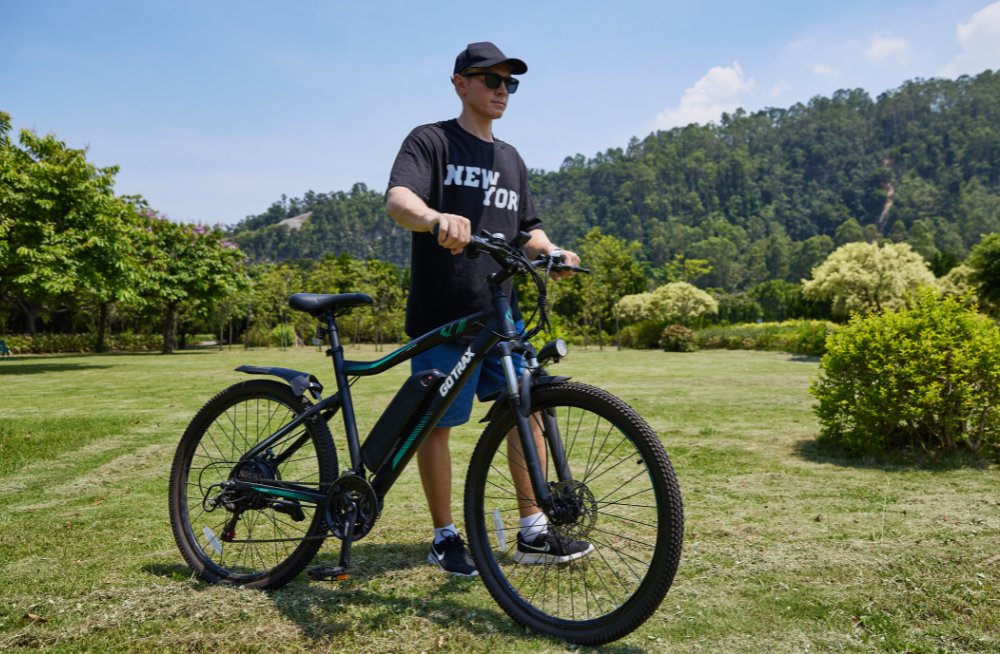
Electric bikes are now a popular way to get around the world, offering a convenient, environmentally friendly way to enjoy the scenery of a city or town.
But how do electric bikes work? In this article, we’ll break down the key components and systems of an electric bike, explain how it works, and explore the benefits it offers riders, especially on Canada’s diverse terrain.
What Is an Electric Bike?
An electric bike is a bicycle that comes with a built-in motor to assist the rider's pedaling efforts. The motor provides extra power, helping you pedal with less effort.
This assistance makes cycling easier, faster, and more enjoyable, particularly on long rides, uphill routes, or in windy conditions. While it still requires pedaling, the electric motor significantly reduces the physical strain on the rider.
Key Components of an Electric Bike
To understand how a mobility device like an electric bike or scooter works, we all need to understand their main components:
1. Electric Motor
The motor is the heart of any electric bike. It provides the extra power needed to assist your pedaling. Most e-bike motors are located in one of three places:
- Front Hub Motor: Located in the front wheel hub, this motor powers the bike forward by turning the front wheel.
- Rear Hub Motor: Situated in the rear wheel hub, this motor is common on e-bikes as it helps provide more balanced power distribution.
- Mid-Drive Motor: Positioned at the bike's bottom bracket, the mid-drive motor powers the pedals directly. This setup is often preferred for its smooth ride and better weight distribution.
2. Battery

The battery is another crucial component of an e-bike. It stores the energy that powers the motor. Most modern e-bike batteries are lithium-ion, similar to the ones used in smartphones. These batteries are lightweight, long-lasting, and efficient.
The size of the battery determines the range of the bike, meaning how far you can travel on a single charge. A typical battery can offer anywhere from 30 to 100 miles (48 to 160 kilometers), depending on the terrain, rider’s weight, and the level of pedal assistance used.
3. Controller
The controller acts as the brain of the e-bike, managing the flow of electricity between the battery and the motor. It controls how much power the motor provides based on your pedaling efforts. Some e-bikes allow you to adjust the power settings, giving you control over how much assistance you want from the motor.
4. Pedal Assist System (PAS)
Most e-bikes come with a Pedal Assist System (PAS), which measures the amount of effort you’re putting into pedaling and adjusts the motor's power accordingly. This system makes the bike feel more like a traditional bicycle while assisting when needed. The PAS can usually be adjusted, allowing you to set it to low, medium, or high levels of support.
5. Throttle (Optional)
Some e-bikes come with a throttle, similar to those found on motorcycles. This allows the rider to control the motor’s power directly without needing to pedal. The throttle can be twisted or pressed to engage the motor, providing an instant boost in power. However, e-bikes with throttles are less common in certain areas, particularly in Canada, where laws often restrict throttle-powered e-bikes.
6. Brakes
Just like traditional bikes, e-bikes need reliable brakes. However, because e-bikes are typically heavier than regular bicycles and can travel faster, they require more powerful braking systems. Hydraulic disc brakes are commonly used on e-bikes because they offer strong stopping power, especially in wet or hilly conditions.
7. Display Panel
The display panel provides important information about the bike’s speed, remaining battery life, power level, and trip details. It also allows the rider to adjust settings like pedal assist levels. This feature makes it easy to track the bike’s performance and ensure you’re getting the most out of your ride.
How Does an Electric Bike Work?
Now that we’ve discussed the key components, let's break down how all of this works together when you're riding an electric bike.
Step 1: Turning on the Bike
When you turn on the e-bike, the controller connects the battery to the motor, and the bike is ready to assist you. Depending on the bike, you might need to press a power button or activate the display panel to get started.
Step 2: Pedaling or Using the Throttle
Once the bike is on, you can either start pedaling or use the throttle (if available). If your bike uses pedal assist, the motor will automatically engage as you begin pedaling. The controller detects the pressure on the pedals and adjusts the motor's power output to match your effort. If you prefer not to pedal, simply use the throttle for a boost of power, and the motor will take over.
Step 3: Adjusting Power Levels
Most e-bikes allow you to adjust the level of assistance. If you want more power, you can increase the pedal assist level. On hilly terrains, or when you need to accelerate quickly, higher levels of assist can make the ride much easier.
Conversely, lower settings will provide a more natural cycling experience, allowing you to exercise more while still receiving some assistance from the motor.
Step 4: Stopping the Bike
When you need to stop, just apply the brakes. The braking system will disengage the motor, ensuring a smooth stop. Many modern e-bikes come with regenerative braking, which helps recharge the battery slightly while braking, though the energy recovered is minimal.
Step 5: Recharging the Battery
After your ride, you’ll need to recharge the e-bike battery. Most e-bike batteries are removable, so you can easily take them indoors to charge.
Depending on the battery size, it can take anywhere from 3 to 6 hours to fully charge. Once the battery is full, your bike is ready for the next adventure.
The Benefits of Riding an Electric Bike
1. Easier to Ride
The most significant benefit of an e-bike is the reduced effort required to pedal. The motor provides assistance, which makes it easier to ride over long distances, climb hills, or navigate rough terrain. For people with limited mobility or fitness levels, e-bikes offer a more accessible way to enjoy cycling.
2. Environmentally Friendly
Electric bikes are eco-friendly, producing zero emissions during operation. They offer a sustainable alternative to cars, reducing traffic congestion and pollution. In Canada, with its vast landscapes and need for sustainable transportation, e-bikes are becoming a popular choice for urban commuters and outdoor enthusiasts alike.
3. Cost-Effective
While the initial cost of an e-bike can be higher than that of a traditional bike, they are more cost-effective than cars in the long run. You won’t need to pay for gas, and maintenance costs are generally lower. Plus, the price of electricity to charge the electric bike battery is much less than the cost of fuel for a car.
4. Health Benefits
Though e-bikes provide motorized assistance, they still require pedaling. This means you can get a great cardiovascular workout, while the motor helps you conserve energy for longer rides. E-bikes are also great for people who are recovering from injuries or want to exercise without overexerting themselves.
Conclusion
Electric bikes are an innovative, practical, and environmentally friendly way to get around. By combining the mechanics of a traditional bicycle with modern electric technology, they make riding more convenient and fun for a wide range of riders. Whether for commuting, leisure, or tackling rugged terrain, electric bikes offer an efficient and easy transportation option.
In this area, GoTrax offers a range of high-performance electric bikes designed for riders who seek efficiency and comfort. Equipped with advanced electric drive systems and durable construction, GoTrax's electric bikes are suitable for a variety of riding needs. Whether you are commuting daily or going on a weekend trip, GoTrax can provide you with a convenient riding experience.
Related reading: Are Electric Bikes Worth It?